Laravel is an open-source PHP web application framework. Its toolkit, libraries, and features help improve development efficiency as users do not need to code all the functionality from scratch.
This popular framework has a large community of developers, which increases support and resource availability. However, new users may be unsure of how to deploy it due to Laravel’s various dependencies and commands.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to deploy the framework on an Ubuntu Virtual Private Server (VPS). This Laravel deployment guide will also explore several tips that help simplify the task.
How to Deploy Laravel Project
In this section, we will explain the steps to deploy Laravel on VPS hosting running on Ubuntu 22.04. Depending on the Linux distro and version, the commands may vary.
1. Choose the Right VPS Hosting
Before getting started with Laravel, purchase a Virtual Private Server hosting plan. When choosing the best VPS hosting plan and provider for your project, consider these aspects:
- Compatibility. Your VPS must support the latest version of the chosen operating system, web server, Laravel, PHP, and other dependencies to run properly.
- access. To enable seamless and secure Laravel deployment the host server must provide full root access via a secure shell (SSH) connection.
- Display. The ideal VPS hosting environment should provide adequate bandwidth and server resources to ensure that the Laravel application performs optimally.
- additional features. Some web hosting providers have features that help simplify the application deployment process, such as control panels and one-click installers.
Hostinger VPS hosting plans are compatible with various Linux distributions, software, and frameworks, including Laravel. Users can install an operating system through hPanel in one click.
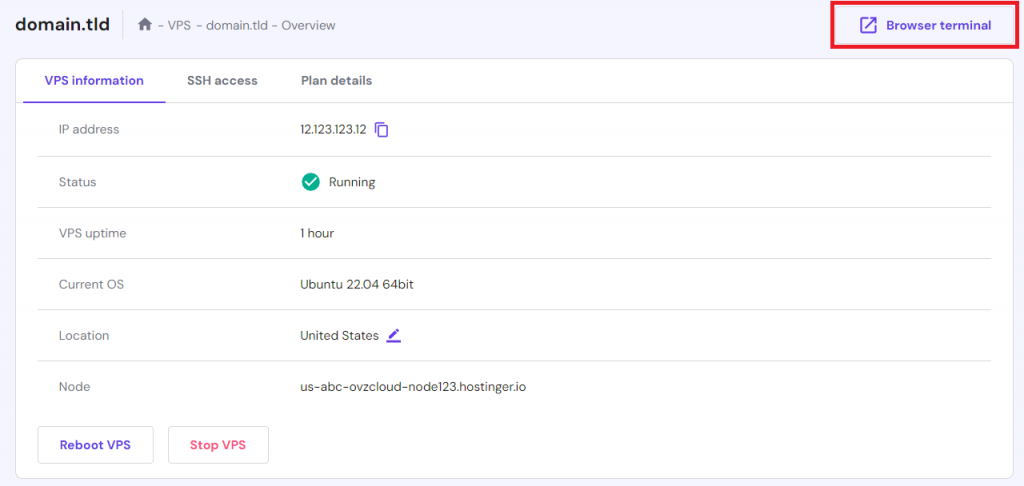
Additionally, all of our VPS plans provide full root access to avoid permission-related issues. Users can also use our built-in browser terminal to connect to their remote servers. It is more convenient than an SSH client because you can run Linux commands directly from your web browser.
Starting at ₹449/month, our VPS solution offers up to 400GB of NVMe storage, 8TB of bandwidth, 32GB of RAM, and 8 vCPU cores, suitable for large-scale enterprise projects. All our plans come with a 30 day money-back guarantee.
2. Prepare the Server for Laravel
After purchasing and installing your VPS, connect remotely via SSH. You can use an SSH application like PuTTY, Terminal, or Hostinger’s browser terminal.
Log in to your server using the root user. On a Hostinger VPS, access the credentials by going to HPanel → VPS on the top menu. Then, go to your VPS plan and go to Overview→SSH Access tab.
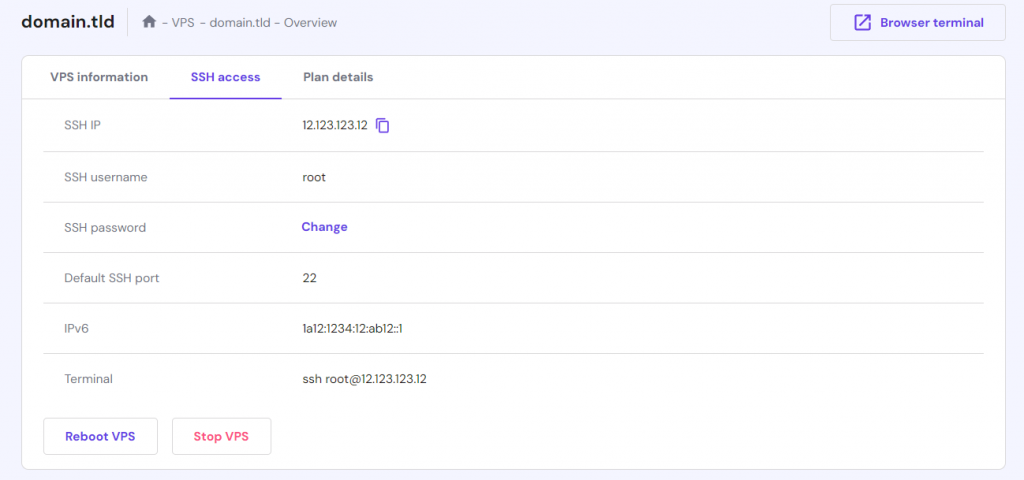
Important! Instead of root, we recommend creating a new account with superuser privileges to avoid accidental destructive command execution.
Laravel requirements include a web server, database, PHP database, and composer. You will also need other software like Git to send application files from your local computer to the remote machine. Here are the steps:
- Update your APT package manager repository using this command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
- Install the web server. In this tutorial, we’ll use Apache:
sudo apt install -y apache2
- Run this command to set up PHP and its extensions:
sudo apt install -y php php-cli php-fpm php-mysql php-xml php-mbstring
- Configure a database. We’ll install MySQL using the following command:
sudo apt install -y mysql-server
- Install Composer to manage Laravel dependencies using this command:
sudo apt install -y composer
- Enter this command to set up the Git version control system:
sudo apt install -y git
If you don’t want to set up a production server manually, buy Laravel Forge. Starting at $12.99/month, this platform provides a centralized area to install and manage all the applications you need for your project.
3. Deploy the Application
Create a virtual host for your Laravel project by setting up a web server configuration file using the Nano text editor. For Apache, run the following command: sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/laravel.conf
Within the file, write the following configuration. Make sure to replace the directory placeholders with the actual path and thedomain.com with your server IP address: ServerName thedomain.com ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot /var/www/html/test-laravel/public < Directory /var/www/html/test-laravel/public> AllowOverride All ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log Combined
Important! The configuration file contents will look different if you use another web server like NGINX.
Deploy the Laravel application project code from your Git repository by running these commands in a series. Replace the URL with the actual link: cd /var/www/htmlsudo git clone
If you haven’t committed your Laravel project files to a repository, read our Git tutorial to learn more about how to do so.
To deploy project files, you can use methods such as the rsync utility or the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) application. However, we recommend version control in Laravel deployments for convenience and security.
Go to your project directory path and run composer install to configure the dependencies: cd test-laravelsudo composer install
If the terminal returns an error message, try running the composer update command. Also, add the –ignore-platform-req=ext-curl option to see if the issue is resolved.
4. Configure the .env File
When you create a Laravel application, Composer will generate a .env.example file template. It stores environment-specific configuration, setting various variables such as database information for your applications.
To set up a .env file for your Laravel project, copy the template below and open it using nano:sudo cp .env.example .envsudo nano .env.
The configuration of this file uses the KEY=VALUE pair syntax. For example, the following entry sets the Laravel database user password:DB_PASSWORD=your_password
To change the configuration, delete the value and replace it with a new one. Press Ctrl + X, Y and Enter to save changes.
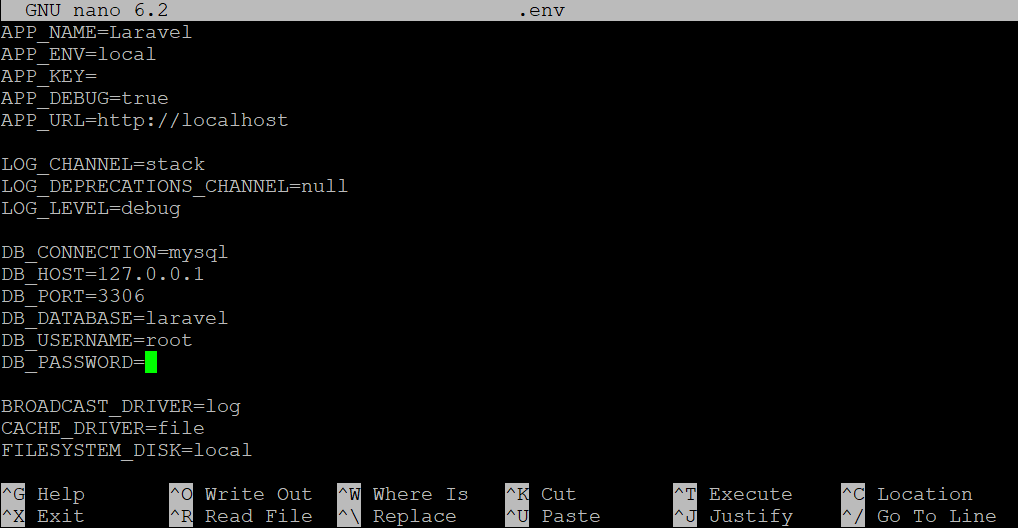
By default, Laravel will set DB_USERNAME as root and leave DB_PASSWORD blank. However, it may generate this error when you run PHP Artisan, the framework command-line utility for database migration.
To resolve this, change the default root password and update the DB_PASSWORD value accordingly. Also, we recommend creating a non-default database and specific user for your current project for easier management.
5. Run the Application
To start your Laravel application, make the project folder executable by changing permissions and ownership: sudo chown -R www-data /var/www/html/test-laravelsudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/test-laravel / storage
Run PHP Artisan to generate the application key and initiate the database migration. Here are the commands: sudo php artisan key: generatesudo php artisan move
Whenever you modify the database schema, update the migration files to maintain a consistent configuration for your app. Check out Laravel’s migration guide to learn more about it.
Disable the default configuration file of virtual host in Apache using the following command: sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
Enable the new virtual host and rewrite module using these commands: sudo a2ensite laravel.confsudo a2enmod rewrite
Restart Apache using systemctl command: sudo systemctl restart apache2
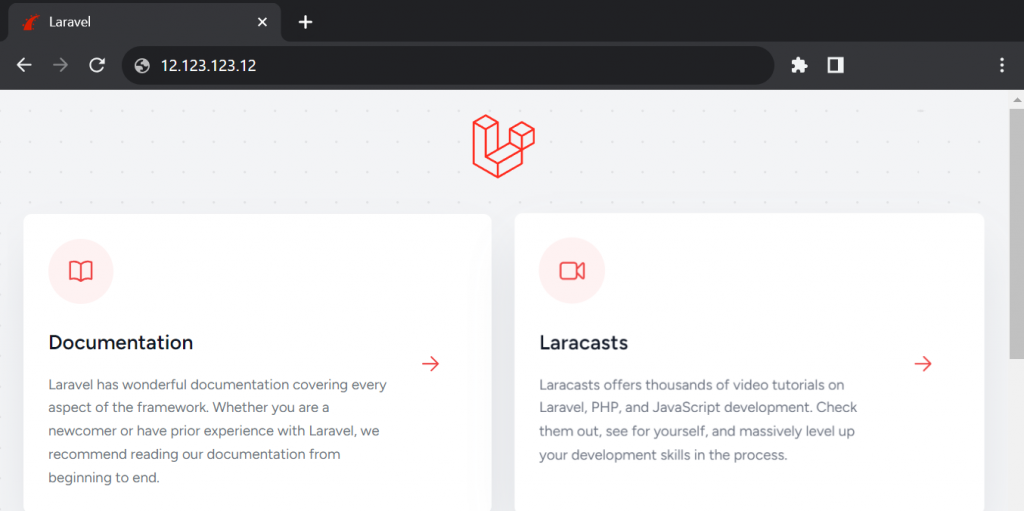
Once the deployment process is complete, enter your VPS IP address or domain name in a web browser to check if the application works correctly. If the files are empty, you should see the Laravel welcome page.
Laravel Deployment Tips and Tricks
In this section, we will discuss several Laravel deployment best practices to help streamline the process.
Use Caching Configuration in Laravel
The Laravel framework lets you store frequently accessed data as cache. It reduces the time required to fetch the information and offloads database queries, improving your web application performance.
It also provides various caching backends and drivers. Users can choose one that best suits their needs and configure it easily through the .env file’s CACHE_DRIVER key.

If you do not specify a cache driver, Laravel will use the file by default. Alternatively, you can set it to Array, Database, Redis or Memcached.
To enable the cache, add the method to your application’s codebase. For example, to store data for a specified period write Cache::put():Cache::put(‘key’, ‘value’, $minutes);
Meanwhile, use the Cache:rememberForever() method to store the cache indefinitely:Cache::rememberForever(‘key’, function);
This framework provides several caching methods for different purposes, such as retrieving, deleting, or incrementing stored data. To learn more about them, check out Laravel’s caching documentation.
To manage the cache, you can run the PHP artisan command in the working directory of your project. For example, enter the following to delete stored data: php artisan cache: clear
Use Automatic Laravel Deployment Tools
Automating Laravel deployment helps save time and effort because without it, the process involves multiple steps. There are various tools and platforms for this task.
You can use continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) services like GitHub Actions or software like Jenkins. They let you automate a custom Laravel deployment pipeline.
To set up automation in GitHub Actions, create a .yml file in your project directory. Define the workflow and its trigger events, such as pushing changes to the master branch. Then, write the task, step, and environment variables. Read the GitHub Actions quick start guide to learn more about it.
For example, you can make it so that whenever a user pushes new code changes to the main branch, the .yml file will automatically run the PHP artisan command to generate the application key and restart your web server. .
Use Hostinger VPS AI Assistant for Easier Deployment
Hostinger offers a free VPS AI Assistant that helps improve your deployment efficiency. You can learn how to deploy a Laravel project on Hostinger and quickly generate instructions and commands for any task using AI prompts for VPS management.
For example, tell the AI assistant, “I want to deploy a Laravel application on my Ubuntu Server using Git. Explain the steps and generate commands for this task.” This will give a comprehensive response, and you can follow the guide and copy-paste the generated commands.
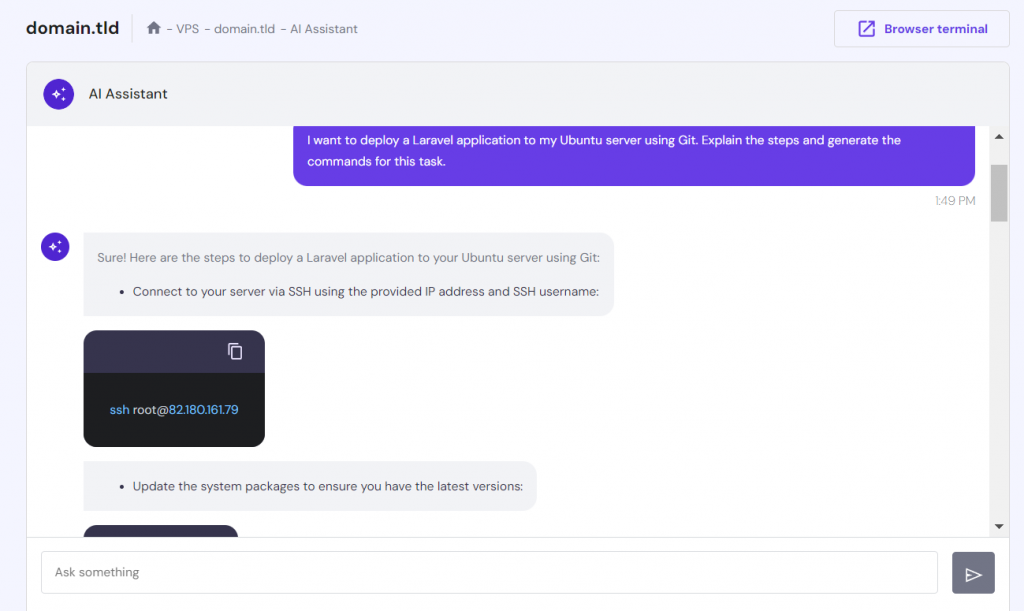
You can also use the AI Assistant to help you troubleshoot errors during the Laravel deployment process. For example, “I am deploying a Laravel application on an Ubuntu server. However, I got an error when running the PHP artisan command to migrate the database. Explain possible causes and solutions.
To access this feature, open your VPS configuration page in hPanel and select AI Assistant from the sidebar.
Important! Like any AI tool, we recommend you always test the generated steps and commands in a development environment first to avoid crashes that could damage your live server.
Utilize Proper Dependency Management
Composer lets developers define their app dependencies in the composer.json file. In addition to simplifying the installation process, it also improves environment stability and version control efficiency.
Run the composer update command to fetch all the dependency patches specified in the file. However, be sure to review new versions before doing so to avoid incompatibility issues or destructive updates.
To access the file, go to your Laravel project root directory. Typically, it is located within the var/www/html/test-laravel path.
The composer.json file only applies to a specific environment. To ensure a clean and efficient project structure, maintain detailed documentation of the dependency configuration of each application or component.
Regularly updating project dependencies ensures that you receive the latest security patches and bug fixes. It also helps to avoid incompatibility issues and version conflicts that can harm the functionality of your application.
Optimize Laravel Performance
Laravel performance optimization helps improve application response and scalability. If you run consumer-facing services, it can also help boost user experience and brand perception.
There are several methods to optimize Laravel performance in an Ubuntu VPS. Here are some of them:
- Enable caching. Laravel provides caching backends and devices to store frequently requested data in temporary storage. This helps reduce server load and database queries.
- Set up a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN caches static content across multiple servers around the world. This helps ensure that your web application performs at its best regardless of the visitor’s location.
- Use queue workers. Queue workers are background processes that handle resource-intensive tasks. They help offload these processes from the main application flow to improve performance.
- Apply eager loading. Eager loading retrieves data related to the requested data on a single query. This helps in reducing the load as there is no need to send information individually to the database.
Also, always track the performance of your web application to ensure that it runs at its best. Doing this allows you to quickly catch potential issues impacting uptime or utilization. Hostinger offers a built-in server resource monitoring feature that can be accessed through hPanel.
Conclusion
Laravel is an open-source PHP web application framework. It offers various toolkits and libraries that help improve development efficiency as users do not need to code all the features from scratch.
In this tutorial, we have explained how to deploy Laravel app on Ubuntu Server. Here’s a recap:
- Buy a VPS hosting plan. Buy a VPS hosting plan with Ubuntu compatibility, latest PHP version, full root access, and SSH support.
- Create a new server. Install Composer, Apache Web Server, PHP, and other software on the production environment. Alternatively, use Laravel Forge to manage them on a single platform.
- Deploy the application. Set up the virtual host by creating an Apache configuration file. Push your app code from a Git repository to the live server.
- Configure the .env file. Copy the .env.example template to your applications folder and change the key-value pair of the .env file to change its settings.
- Run the Laravel application. Change permissions and ownership of the project folder. Run composer install and PHP artisan commands, then disable Apache’s default virtual host.
To improve Laravel application deployment efficiency, use Hostinger’s VPS AI Assistant, automation tools, and Composer Dependency Manager. Additionally, set up a CDN, enable caching, and optimize database queries to improve your application’s performance.
How to Deploy Laravel FAQ
In this section, we will answer several common questions about deploying a Laravel project.
What Do I Need to Deploy a Laravel Project?
To deploy Laravel apps, you need a server running a compatible operating system like Ubuntu. You also need a number of dependencies like web server, PHP, PHP extensions, composer, Git, and databases.
It is also possible to use NGINX or Apache. Meanwhile, Laravel’s popular databases include MySQL and MongoDB.
Can I Deploy Multiple Laravel Applications on the Same Server?
Yes, you can deploy multiple applications in Laravel Server with a dedicated directory, dependencies, and configuration environment.
To do this, create separate folder for Laravel applications within /var/www/html path. Set up dedicated virtual hosts for each project and copy the .env file to each directory.
Can I Scale My Laravel Application?
Yes. You can apply common scaling methods such as configuring load balancers, upgrading server resources, and installing caching mechanisms such as Redis or Memcached.
Furthermore, this framework has a built-in queuing system that offloads resource-demanding tasks from the main flow. This helps improve performance to scale Laravel applications.
