Google recently added Interaction to Next Paint (INP) to the Google Search Console report. Google plans to add INP as part of the Core Web Vitals metrics in March 2024, replacing First Input Delay (FID). The Search Console reports now include the new INP data, providing valuable insights to website owners as they prepare for the upcoming update next year.
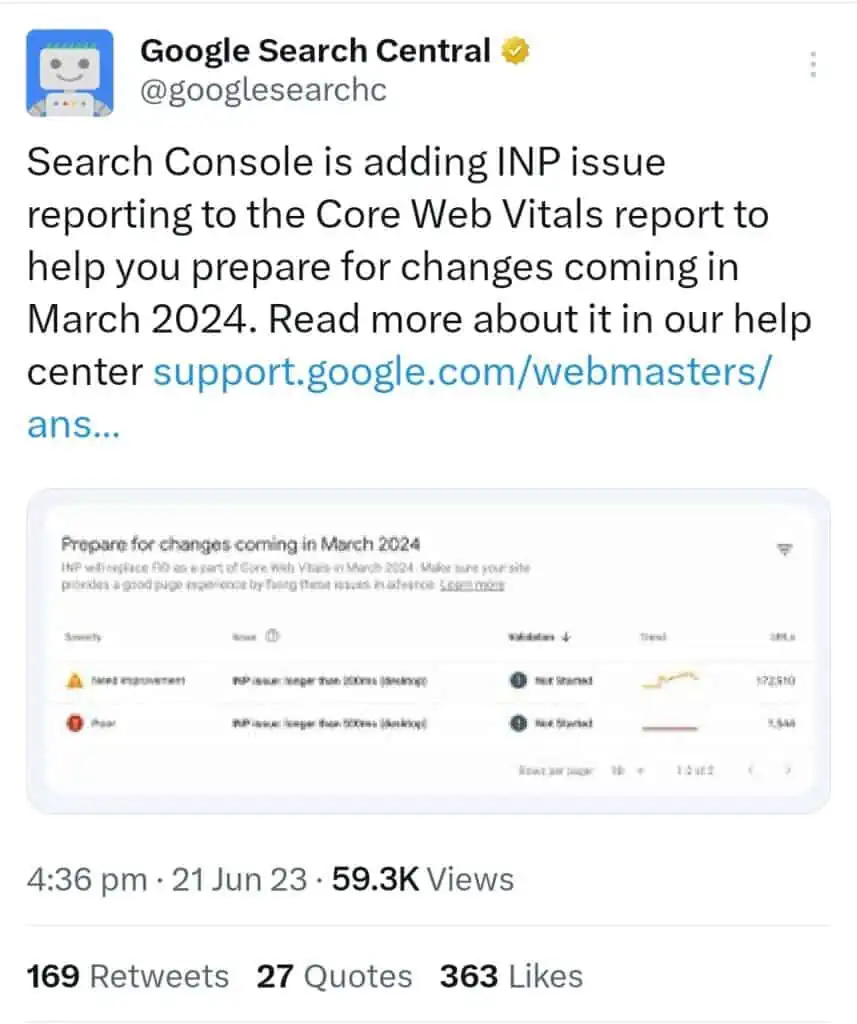
This additional information will help website owners assess their INP performance, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary optimizations to enhance the user experience.
Having access to INP data within the Search Console reports will enable website owners to effectively monitor their progress and ensure readiness for the update.
what is FID ?

FID, or First Input Delay, is a metric that measures the responsiveness and interactivity of a web page. It quantifies the time delay between when a user first interacts with the page (such as clicking a button or tapping a link) and when the browser responds to that interaction by executing the associated JavaScript or other event handlers.
FID is an important metric because it directly affects the user experience. A low FID indicates that the page is highly responsive and provides a smooth interaction for users, while a high FID means there is a noticeable delay in the page’s responsiveness, leading to a poor user experience.
To provide a good user experience, websites should aim for an FID of less than 100 milliseconds (ms). An FID between 100 ms and 300 ms is considered needs improvement, and anything above 300 ms is considered poor.
What is INP ?
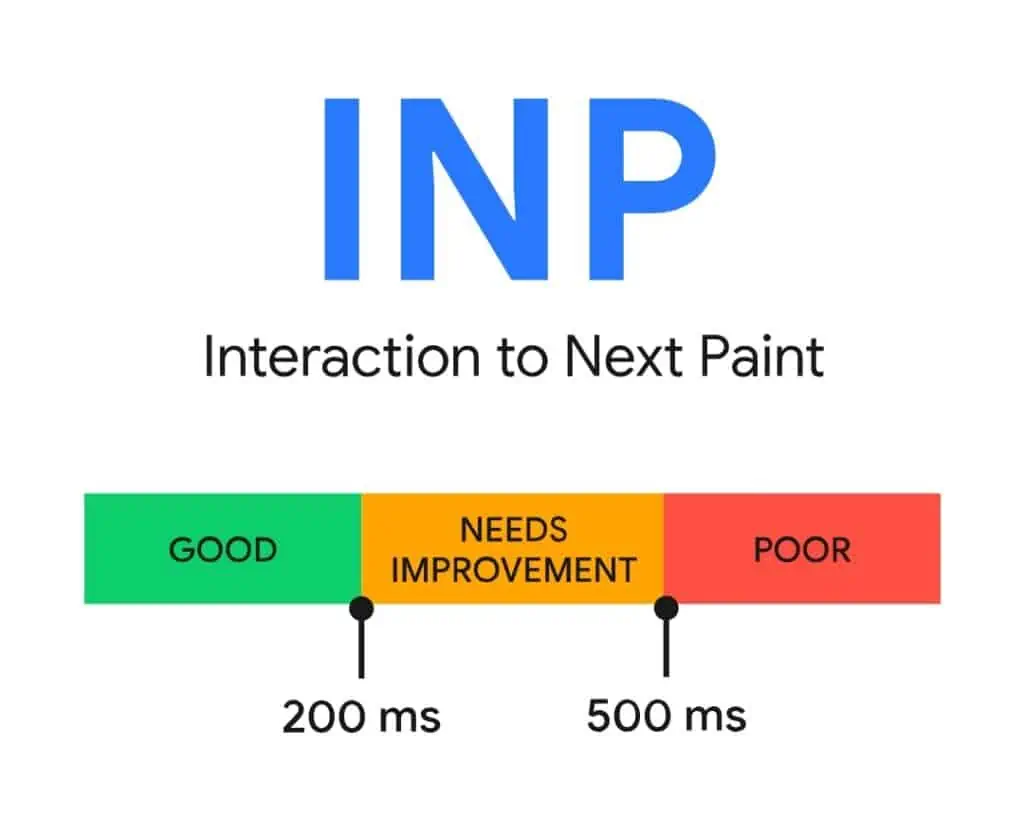
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is a Core Web Vitals metric designed to evaluate a web page’s responsiveness to user interactions during a user’s visit. It measures the latency of all qualifying interactions that occur during the user’s session. The INP value is determined by identifying the longest observed interaction, excluding outliers.
To deliver an optimal user experience, websites should aim for an INP of 200 milliseconds or less. To ensure that most users experience an INP of 200 milliseconds or less, it is recommended to evaluate the 75th percentile of page loads separately for mobile and desktop devices.
Upcoming changes in Core Web Vitals
Google’s implementation of INP issue reporting in Search Console aims to streamline the process for users, facilitating a seamless transition.
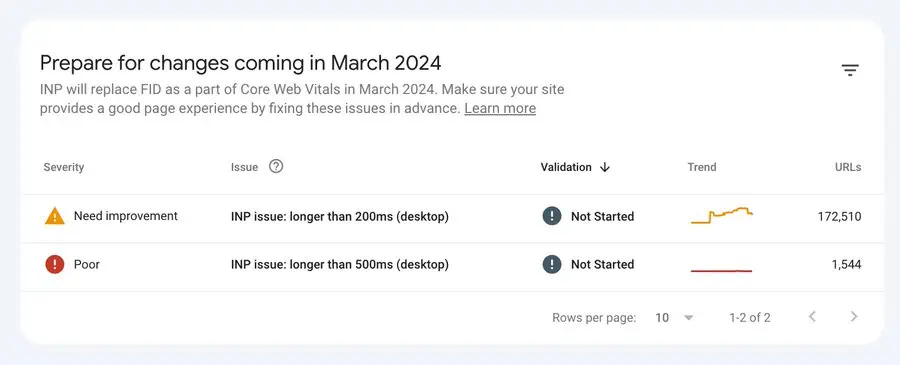
By providing website owners with sufficient time and essential tools, Google ensures that they have everything necessary to optimize their web pages before the March 2024 deadline. Websites that have already been optimized for speed and performance are likely to experience positive INP scores right away. However, websites that have not actively monitored these metrics may encounter issues and could potentially face a decline in rankings once the change is implemented.
It is crucial for website owners to proactively monitor and address any performance-related issues to ensure a smooth transition and maintain or improve their rankings. In my opinion, websites should have a minimalist look and focus on user experience, as this can directly impact rankings. By actively focusing on optimizing INP and other Core Web Vitals metrics, websites can enhance user experience and mitigate any negative impact on rankings.
How to Optimize Your Website for INP, the New Core Web Vital Metric for Responsiveness
Reduce the amount of JavaScript and CSS that your website loads.
The more JavaScript and CSS that your website loads, the longer it will take for the browser to render the page and respond to user interactions. You can use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse to identify and eliminate unused JavaScript and CSS.
Use a content delivery network (CDN) to serve your static assets.
A CDN can help to improve the performance of your website by delivering your static assets (such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files) from servers that are located closer to your users.
Optimize your images.
Large images can slow down your website’s loading time and responsiveness. You can use a tool like TinyPNG or Smush to compress your images without sacrificing quality.
Use lazy loading to defer the loading of non-critical resources.
Lazy loading allows you to defer the loading of non-critical resources, such as images below the fold, until they are needed. This can help to improve the initial loading time of your website and make it more responsive.
Avoid using long-running scripts.
Long-running scripts can block the main thread of the browser, preventing it from responding to user interactions. You can use tools like Chrome DevTools to identify and break up long-running scripts.
What are your thoughts on the recent changes in Search Console? Let us know in the comment section.
For more SEO news like this, bookmark our site and subscribe to our newsletter.
